Introduction
Overhead cranes occupy a central position in industrial and building sites where the material handling processes are not only performed easily, but also safely. Another major system which allows a smooth running process of these cranes is the conductor bar system. Conductor bars (or bus bars or power rails) are used to transmit power reliably and with continuity into the crane motors, controls and other electrical systems. They can be designed, manufactured, and durable that could have a lot to do with the crane performance, safety, and maintenance needs.
The article will focus on the importance of conductor bars in crane systems, the benefits they have compared to other power supply sources and tips that can be used to pick the right conductor bars and maintain them.
What Are Conductor Bars?
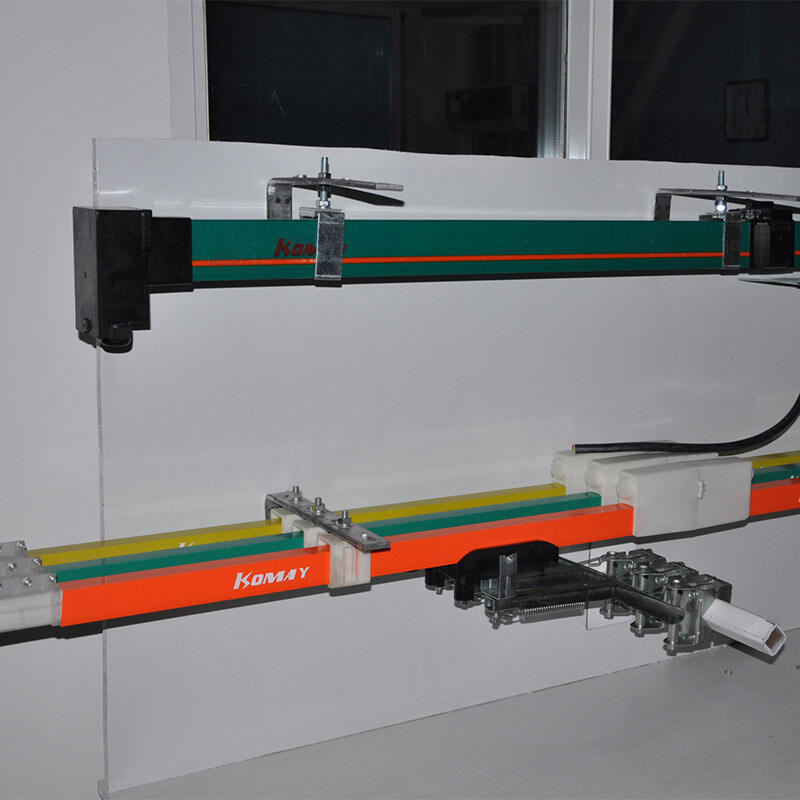
Conductor bars by Wuxi Komay Electric Equipment Co., Ltd. are stiff or bendable energized rails that embrace electrical power down the track of the crane. They are designed of high conductive material (usually copper or aluminum) and packaged with or in a protective housing to avoid the effects of dust and moisture as well as physical damage. Conductor bars are placed along the crane runway, on which power collectors on the crane continually stay in contact as the crane travels.
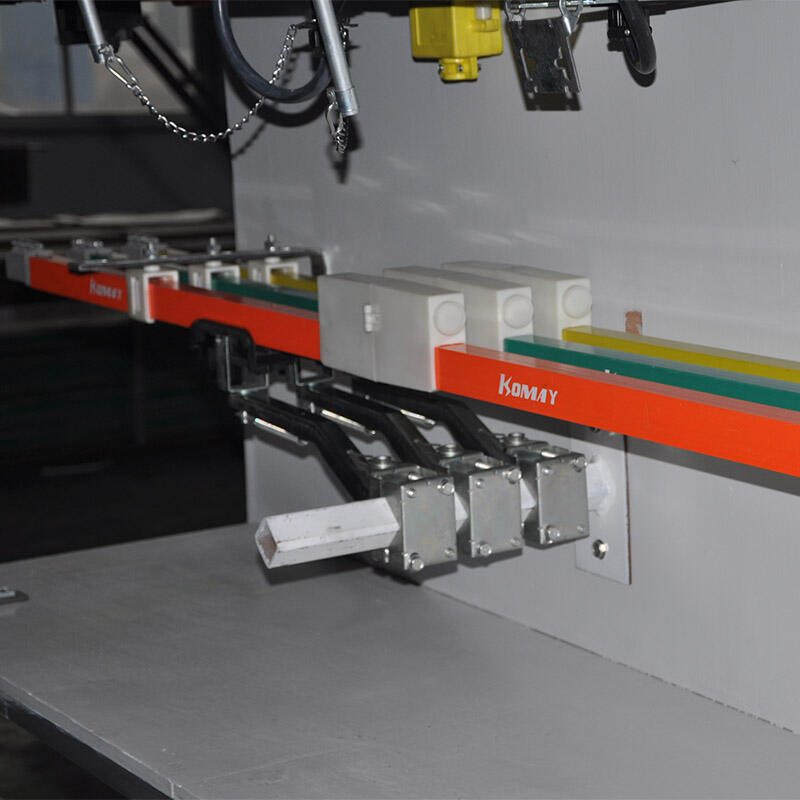

Key Functions of Conductor Bars in Crane Systems
Continuous Power Supply
Conductor bars, unlike cable reels or festoon systems, can offer the continuous power required without the possibility of cable abrasion, entanglement, or break. This means that it operates consistently and in high-duty-cycle applications.
Enhanced Safety
There is reduced electrical shocks, short circuits and risks of fire propagation with enclosed conductor bar systems. They have good insulation and protective covers such that they are not touched by accident into live parts.
Reduced Maintenance
The life time of conductor bars is longer than that of the trailing cables, the latter experiencing frequent inspection and being replaced often, caused by mechanical wear.
High Current Capacity
Conductor bars can be made with high electrical capacity to drive heavy-duty cranes such as those operating at steel mills, in port, and in factories.
Adaptability to Harsh Environments
Outside cranes, chemical plants and other severe industrial conditions are best served by specialized conductors bars coated with corrosion inhibitors (or stainless-steel compounding).
Comparison with Alternative Power Supply Methods
Conductor bars are quite effective although other means of supplying power are:
Festoon Systems (Cable Reels): These are flexible cables that extends /retracts itself as the crane moves. They are economical when used over small distances but they are prone to wear out and they need frequent repairs.
Drag Chains (Energy Chains): Ensures the protection of cables by directing them in a chain-like structure, are moderate-duty applications, less effective with the high-speed cranes.
Condutor bars are more durable, safer and efficient compared to these alternatives especially where heavy industries are concerned.
Best Practices for Selecting and Maintaining Conductor Bars
Material Selection
Copper conductor bars are more costly, yet more conductive and corrosion resistant.
Aluminum conductor bars are light in weight and they are cheap to purchase but need good insulation to inhibit rusting.
Proper Installation
This should be aligned carefully so as to prevent uneven wearing of collector shoes.
Electrical leakage should be avoided by using insulated supports.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Watch out with dust build up, oxidation or physical damage.
Periodically lubricate collector shoes to cut down friction.
Measure voltage drop on large bar runs of conductors to maintain continuity of power.
Environmental Considerations
In wet or corrosive applications, then select IP-rated, or stainless-steel conductor bars.
Where there is an explosive atmosphere, use flameproof or intrinsically safe.

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 HR
HR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 HI
HI
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RO
RO
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 SV
SV
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 LV
LV
 LT
LT
 SR
SR
 SK
SK
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 SQ
SQ
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 BN
BN
 MN
MN
 KK
KK
 KY
KY